photo credit: Oksana Taran
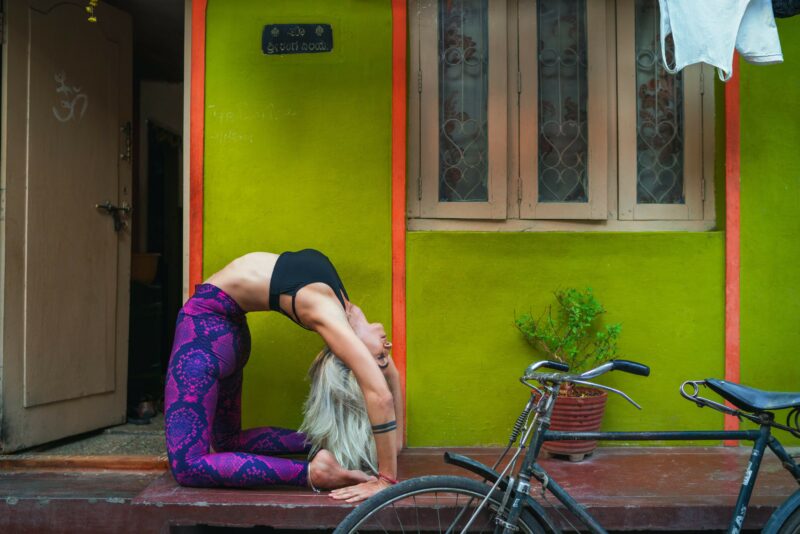

photo credit: Oksana Taran
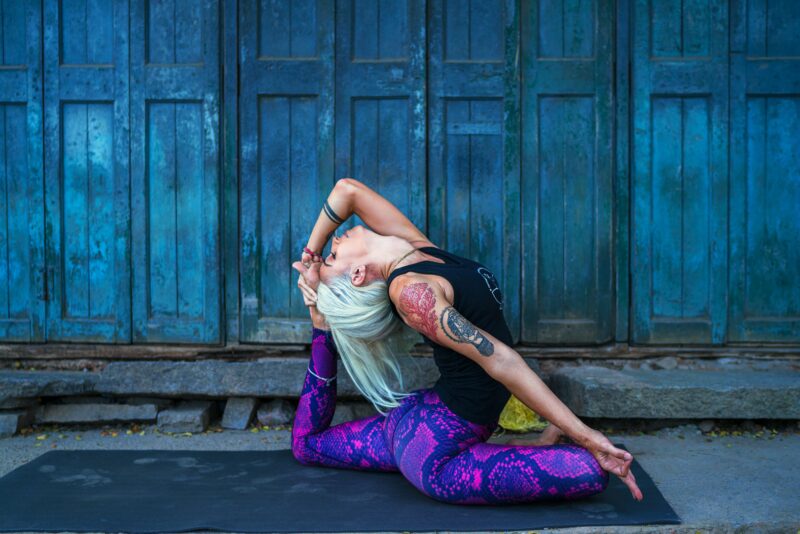

photo credit: Oksana Taran
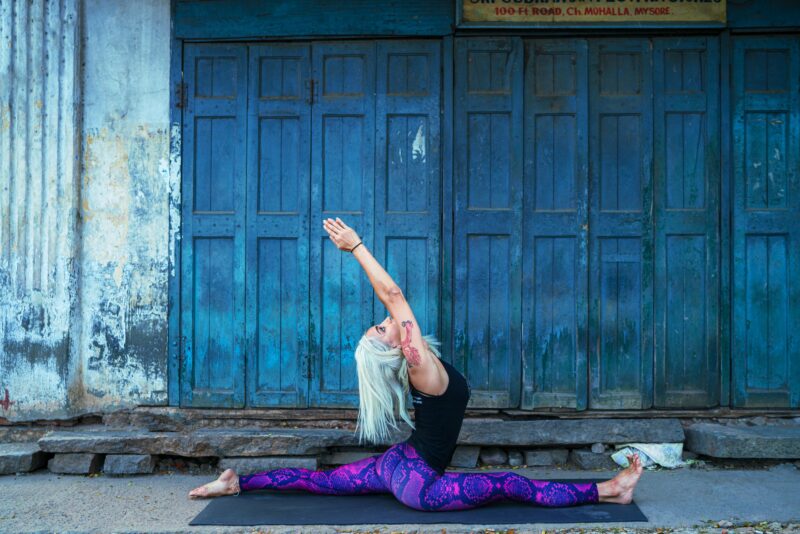

photo credit: Oksana Taran
photo credit: Oksana Taran
photo credit: Oksana Taran

photo credit: Oksana Taran

photo credit: Oksana Taran

photo credit: Oksana Taran

photo credit: Oksana Taran
photo credit: Oksana Taran
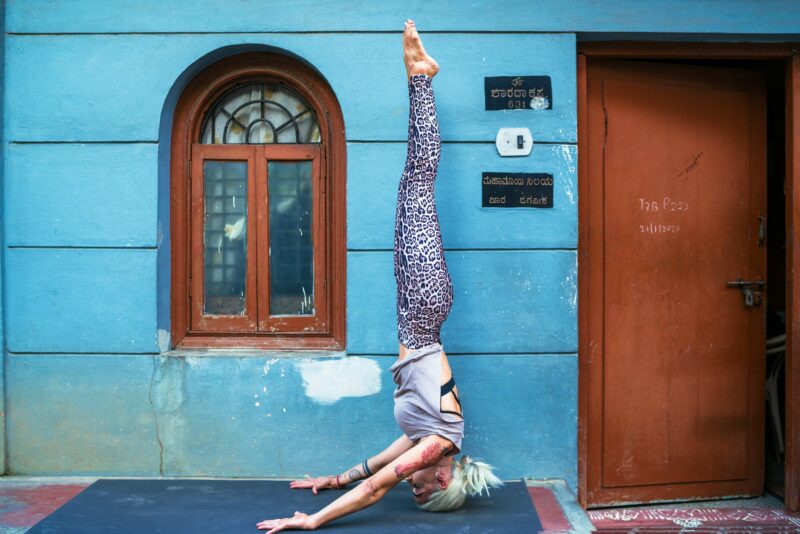
photo credit: Oksana Taran

photo credit: Oksana Taran

photo credit: Oksana Taran

photo credit: Oksana Taran

photo credit: Oksana Taran
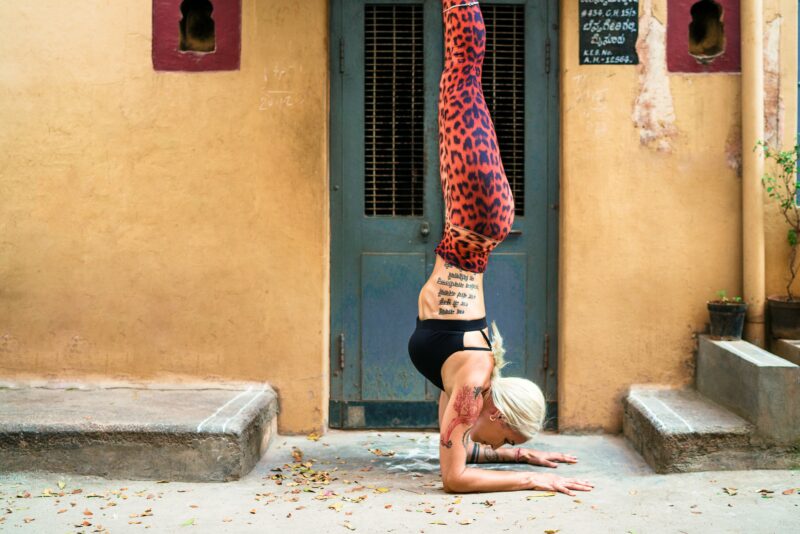

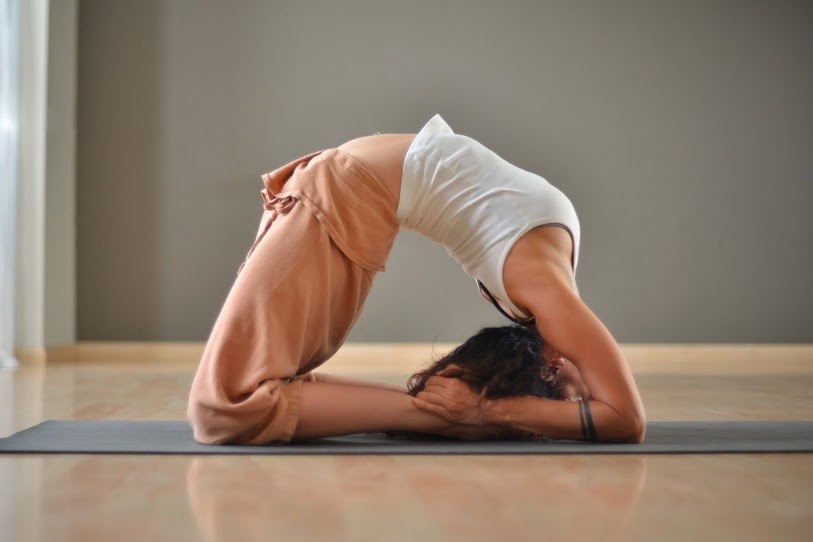
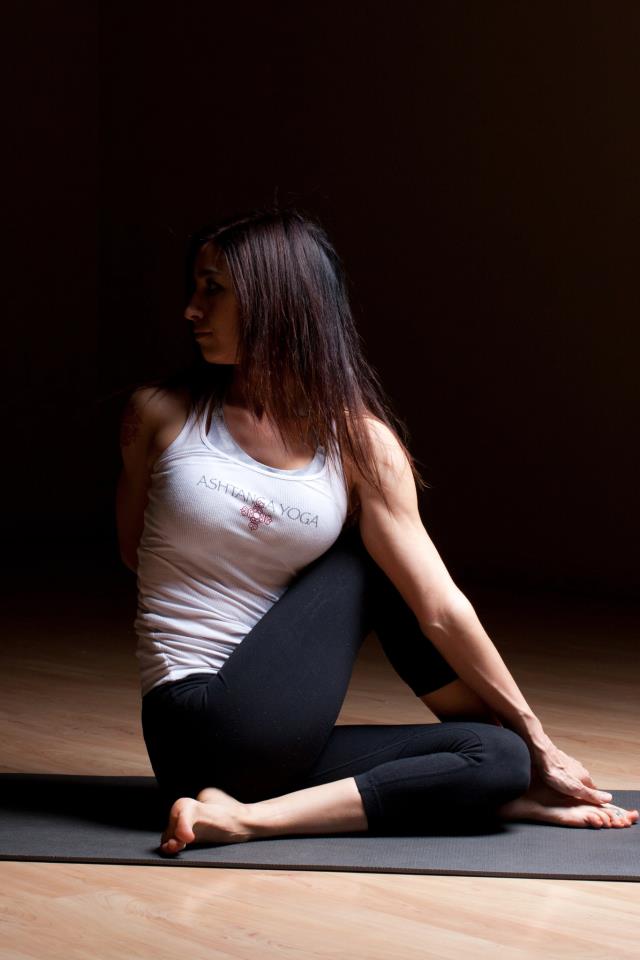
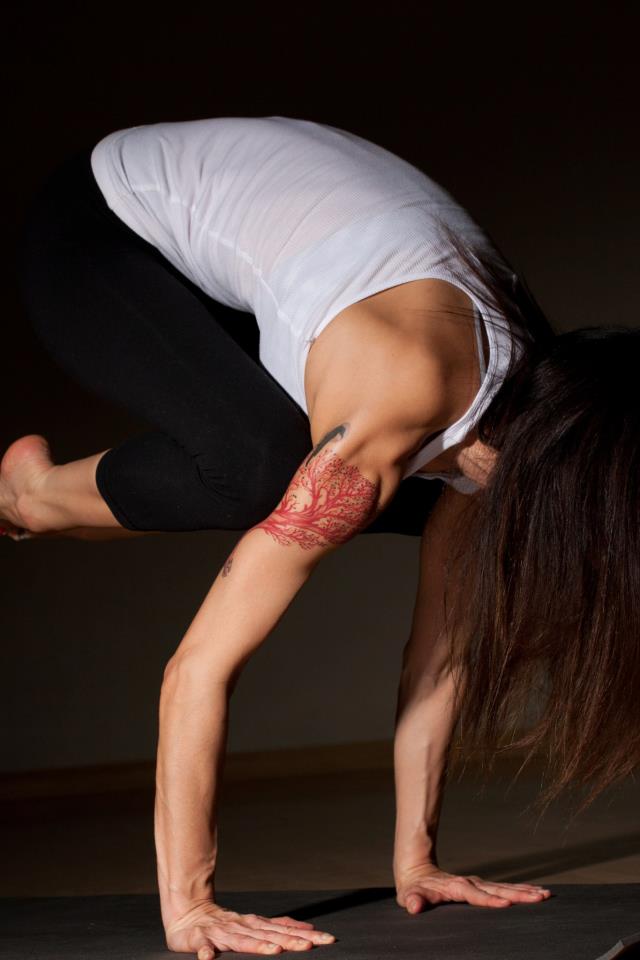
Photo Credit: Ash Christensen

Photo Credit: Ash Christensen

Photo Credit: Ash Christensen

Photo Credit: Ash Christensen
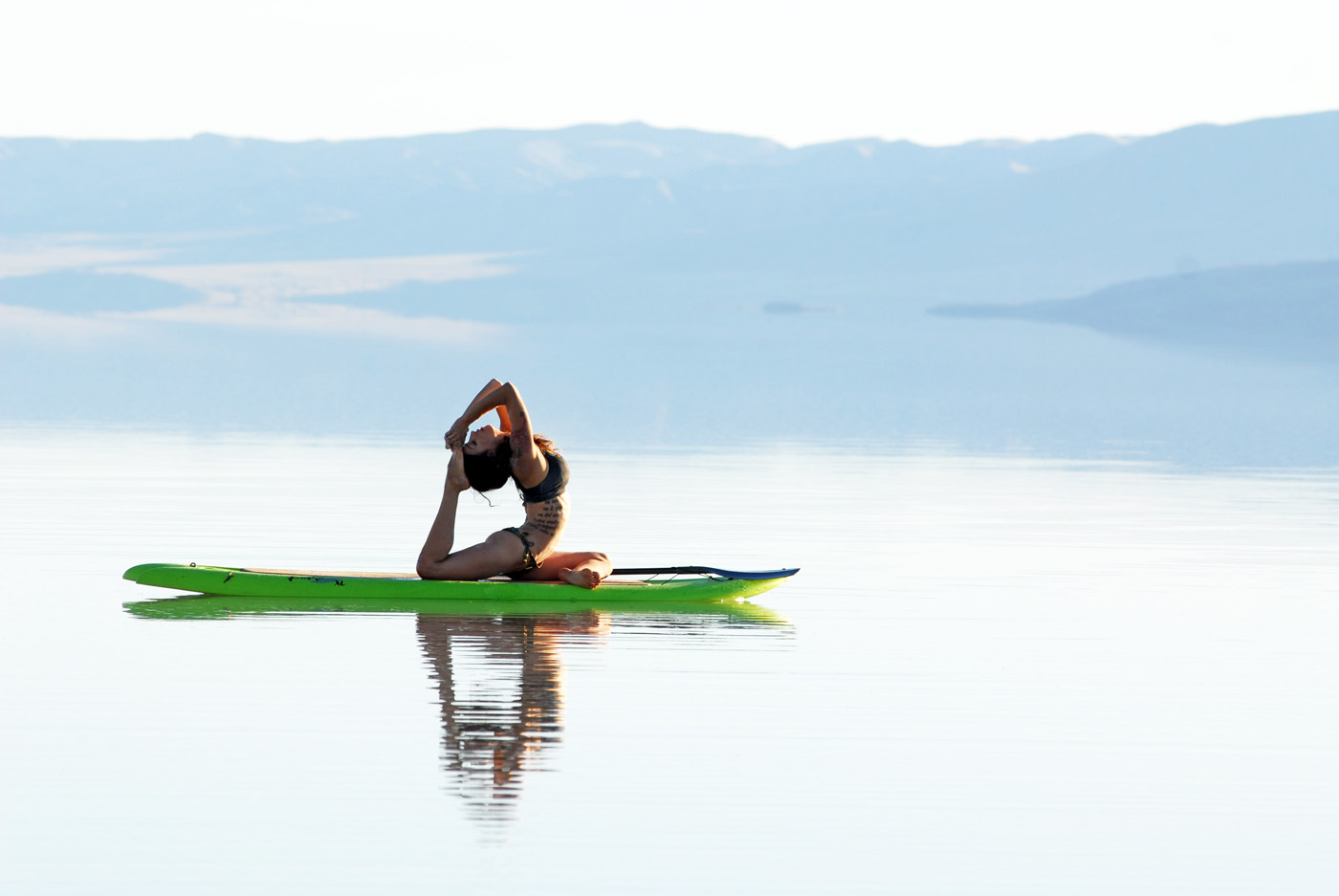

Photo Credit: Ash Christensen
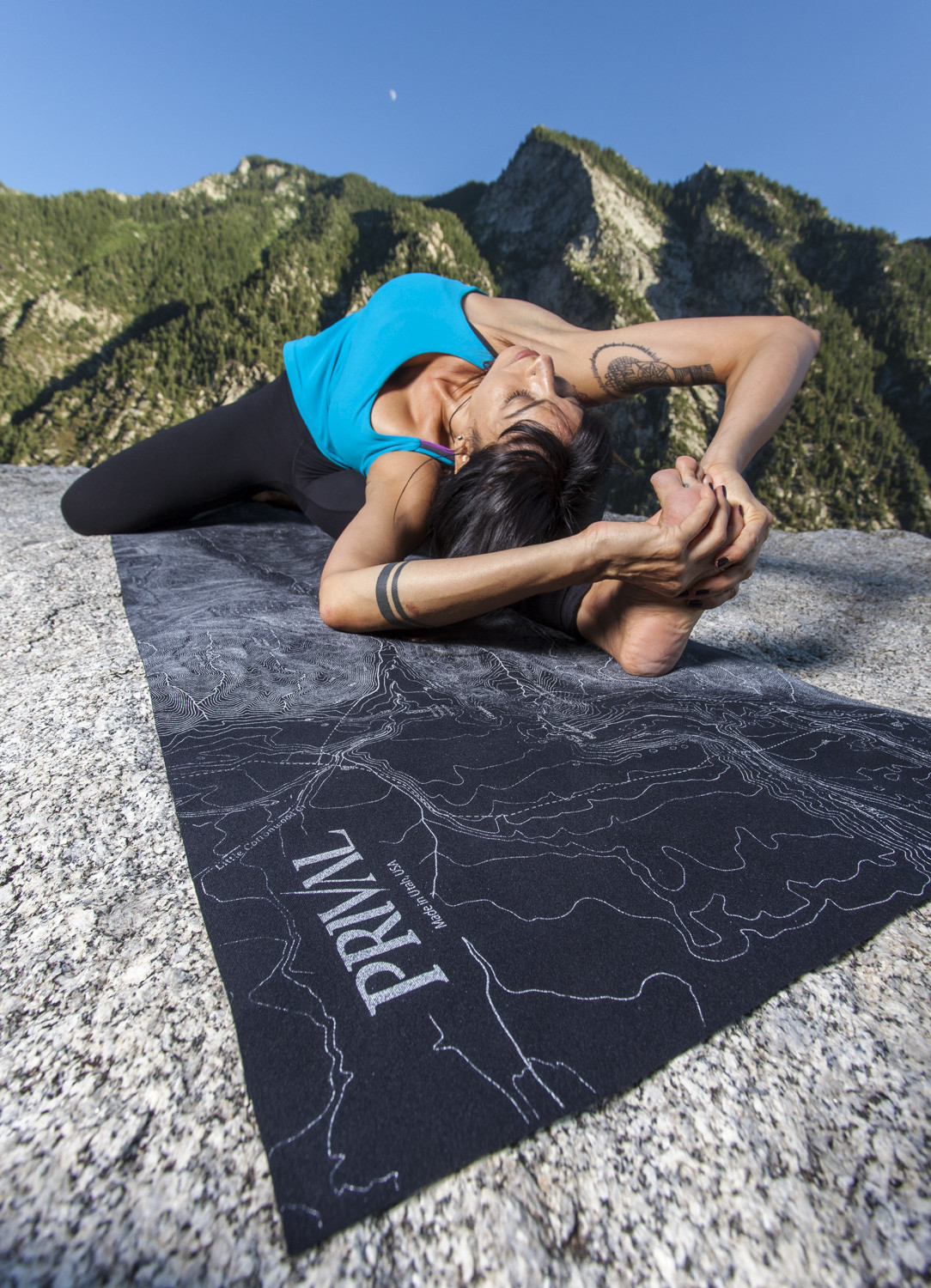

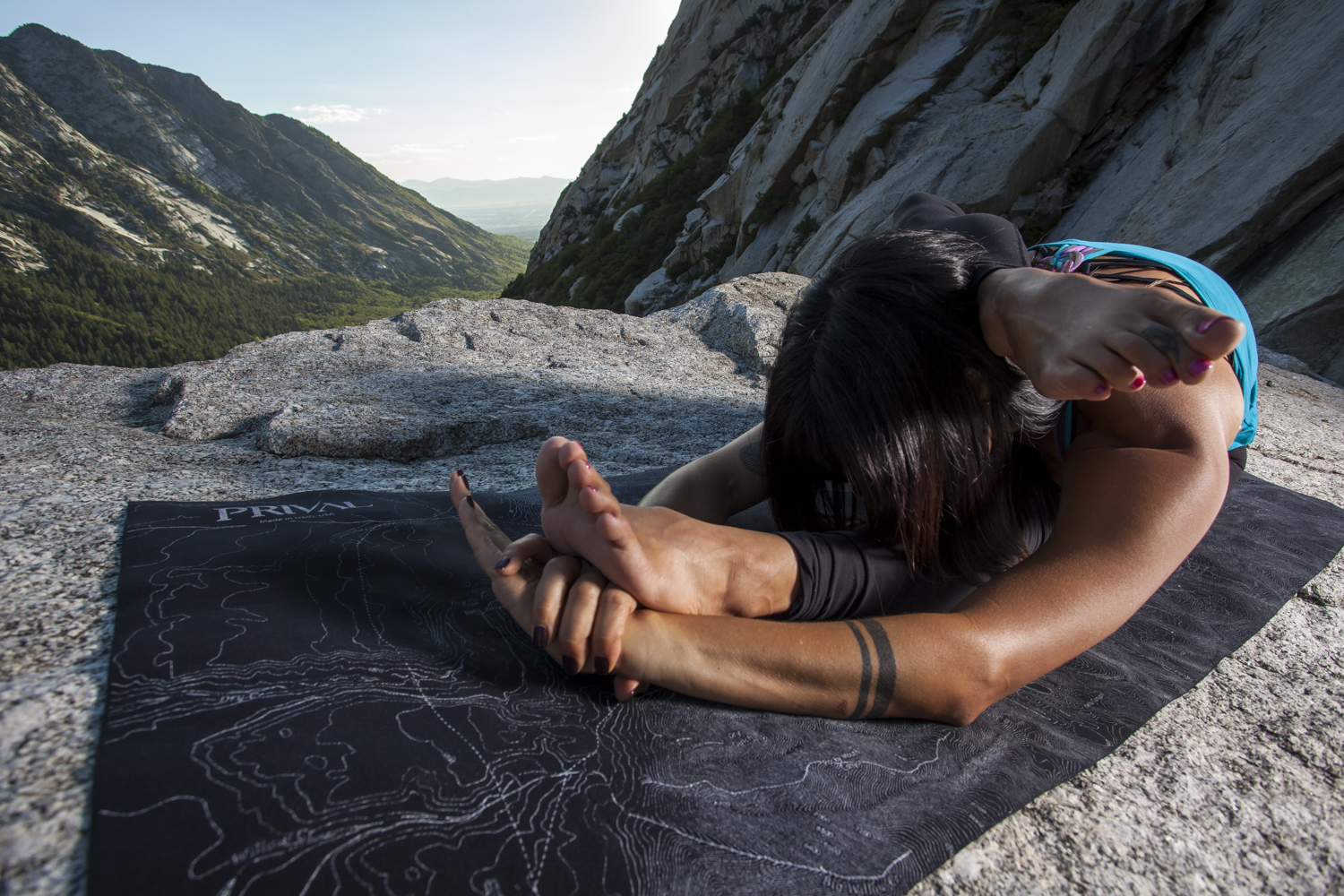
Photo Credit: Ben Girardi Photography and Tony Pavlantos of Prival USA for this photo set taken in Little Cottonwood Canyon with the amazing LCC Travel Yoga mat!
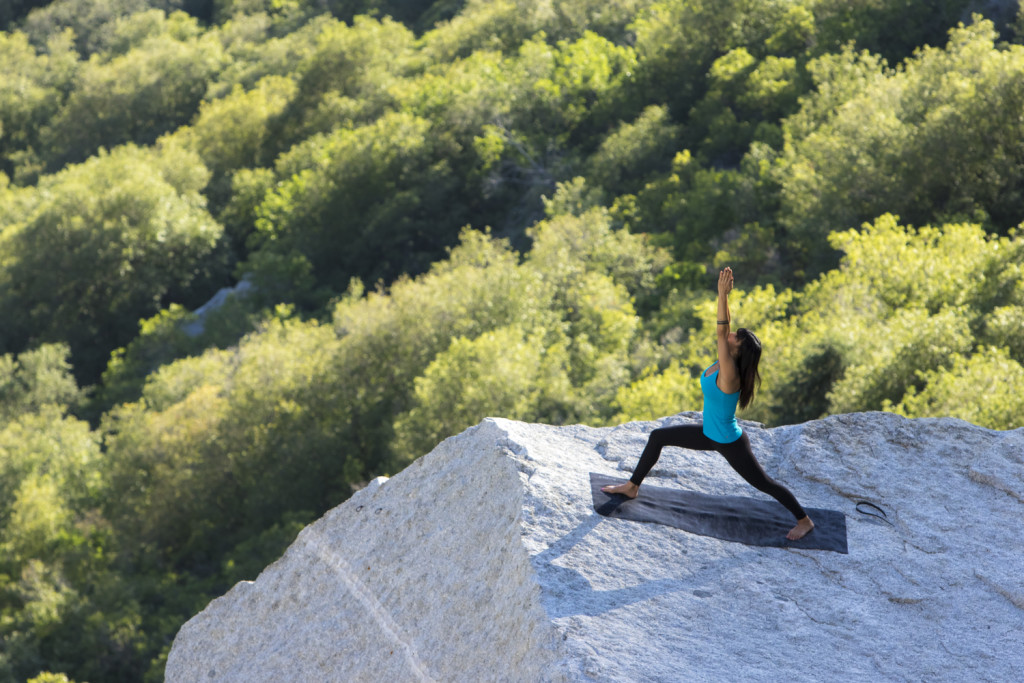

PHOTO CREDIT: BEN GIRARDI PHOTOGRAPHY AND TONY PAVLANTOS OF PRIVAL USA
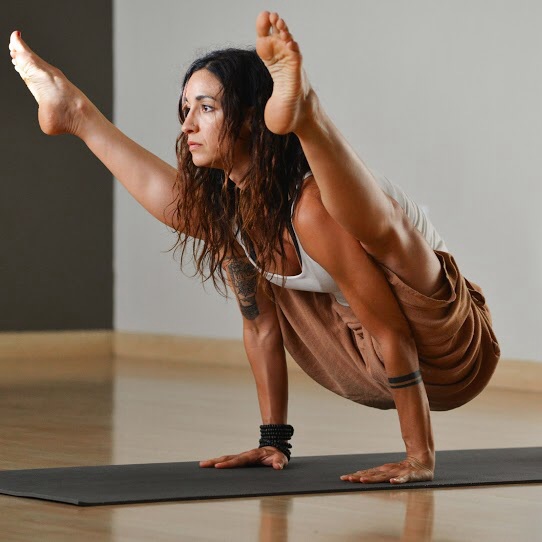

Photo Credit: Elliot Layda

Photo Credit: Elliot Layda
Credit for photos below: Howie Oren

Stories and folk traditions present Hanuman as a divine being, as a descendent of deities, and as an avatar of Shiva.He emerged as a champion of those religiously persecuted, expressing resistance, a yogi, an inspiration for martial artists and warriors, a character with less fur and increasingly human, symbolizing cherished virtues and internal values, and worthy of devotion in his own right.
Hanuman has many attributes:
- Chiranjivi (immortal): various versions of Ramayana and Rama Katha state towards their end, just before Rama and Lakshmana die, that Hanuman is blessed to be immortal. He will be a part of humanity forever, while the story of Rama lives on.
- Kurūp and Sundar: he is described in Hindu texts as kurūp (ugly) on the outside, but divinely sundar (beautiful inside).
- Kama-rupin: He can shapeshift, become smaller than the smallest, larger than the largest adversary at will. He uses this attribute to shrink and enter Lanka, as he searches for the kidnapped Sita imprisoned in Lanka. Later on, he takes on the size of a mountain, blazing with radiance, to show his true power to Sita.
- Strength: Hanuman is extraordinarily strong, one capable of lifting and carrying any burden for a cause. He is called Vira, Mahavira, Mahabala and other names signifying this attribute of his. During the epic war between Rama and Ravana, Rama’s brother Lakshmana is wounded. He can only be healed and his death prevented by a herb found in a particular Himalayan mountain. Hanuman leaps and finds the mountain. There, states Ramayana, Hanuman finds the mountain is full of many herbs. He doesn’t know which one to take. So, he lifts the entire Himalayan mountain and carries it across India to Lanka for Lakshmana. His immense strength thus helps Lakshmana recover from his wound.This legend is the popular basis for the iconography where he is shown flying and carrying a mountain on his palm.
- Innovative: Hanuman is described as someone who constantly faces very difficult odds, where the adversary or circumstances threaten his mission with certain defeat and his very existence. Yet he finds an innovative way to turn the odds. For example, after he finds Sita, delivers Rama’s message, and persuades her that he is indeed Rama’s true messenger, he is discovered by the prison guards. They arrest Hanuman, and under Ravana’s orders take him to a public execution. There, the Ravana’s guards begin his torture, tie his tail with oiled cloth and put it on fire. Hanuman then leaps, jumps from one palace rooftop to another, thus burning everything down.
- Bhakti: Hanuman is presented as the exemplary devotee (bhakta) of Rama and Sita. The Hindu texts such as the Bhagavata Purana, the Bhakta Mala, the Ananda Ramayana and the Ramacharitmanas present him as someone who is talented, strong, brave and spiritually devoted to Rama.The Rama stories such as the Ramayana and the Ramacharitmanas, in turn themselves, present the Hindu dharmic concept of the ideal, virtuous and compassionate man (Rama) and woman (Sita) thereby providing the context for attributes assigned therein for Hanuman.
- Learned Yogi: In the late medieval texts and thereafter, such as those by Tulasidas, attributes of Hanuman include learned in Vedanta philosophy of Hinduism, the Vedas, a poet, a polymath, a grammarian, a singer and musician par excellence.
- Remover of obstacles: in devotional literature, Hanuman is the remover of difficulties.























